Advantages of Belt Suspension in Traction Elevators
Jun 3, 2025

Innovation and efficiency
by Ing. Alberto Mantovani
Introduction
In today’s technological landscape related to traction elevators, the pursuit of energy efficiency, compactness and space optimisation represents a constant challenge for designers and manufacturers. Among the most innovative and promising solutions, belt suspension systems clearly stand out, enabling the use of exceptionally small pulleys as small as 75 mm in diameter. This article analyses in detail the benefits derived from adopting this technology, comparing it with traditional systems and assessing its tangible impacts in terms of energy savings, cost reduction, maintenance and space management.
Importance of Small-Diameter Pulleys
First of all, the dimension of a gearless machine is strongly influenced by torque. Torque is the main parameter to identify gearless size. The bigger the torque, the bigger and heavier the gearless.
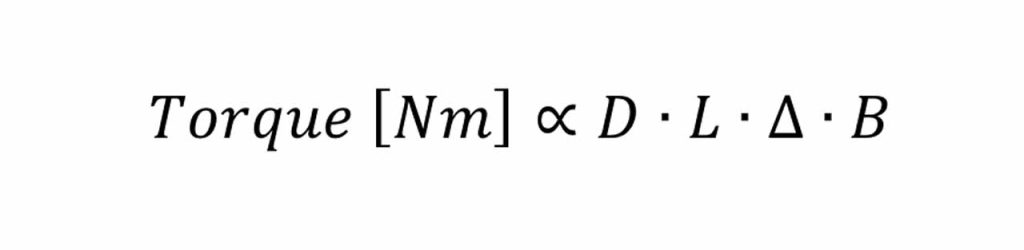
Where D and L are the external diameter and length of the rotor (at the end of the size) and ∆·B are the current and flux densities depending mainly on the grade of materials used (winding, magnets, stator).
Let’s look at what factors determine the torque in an elevator:
where (neglecting ropes weight and frictions)
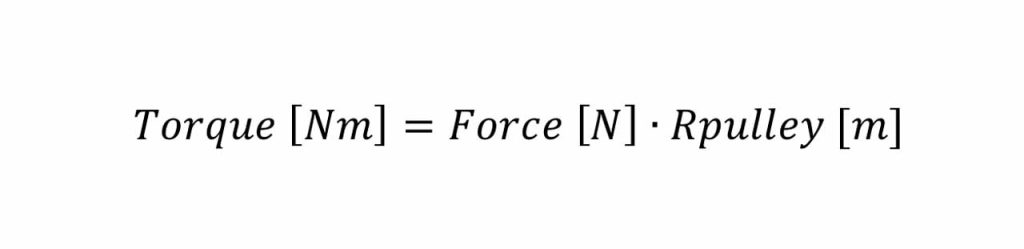
Therefore, force depends only on the installation parameters such as Load (Q), Cabin Weight (P), Counterweight (CWT) and roping.
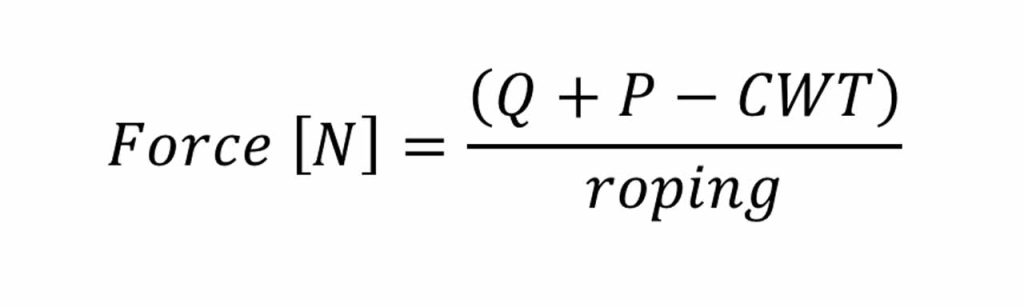
As clearly indicated by the relationship between torque and pulley diameter, pulley size directly affects the torque required for moving the elevator car. The formula Torque = Force × Rpulley clearly demonstrates how a smaller pulley diameter reduces the required torque. Consequently, the ability to adopt small pulleys (down to 75 mm), made possible by the belt suspension system, offers significant design advantages. This allows for reduced torque requirements and consequently the use of much smaller, lighter and more compact gearless motors.
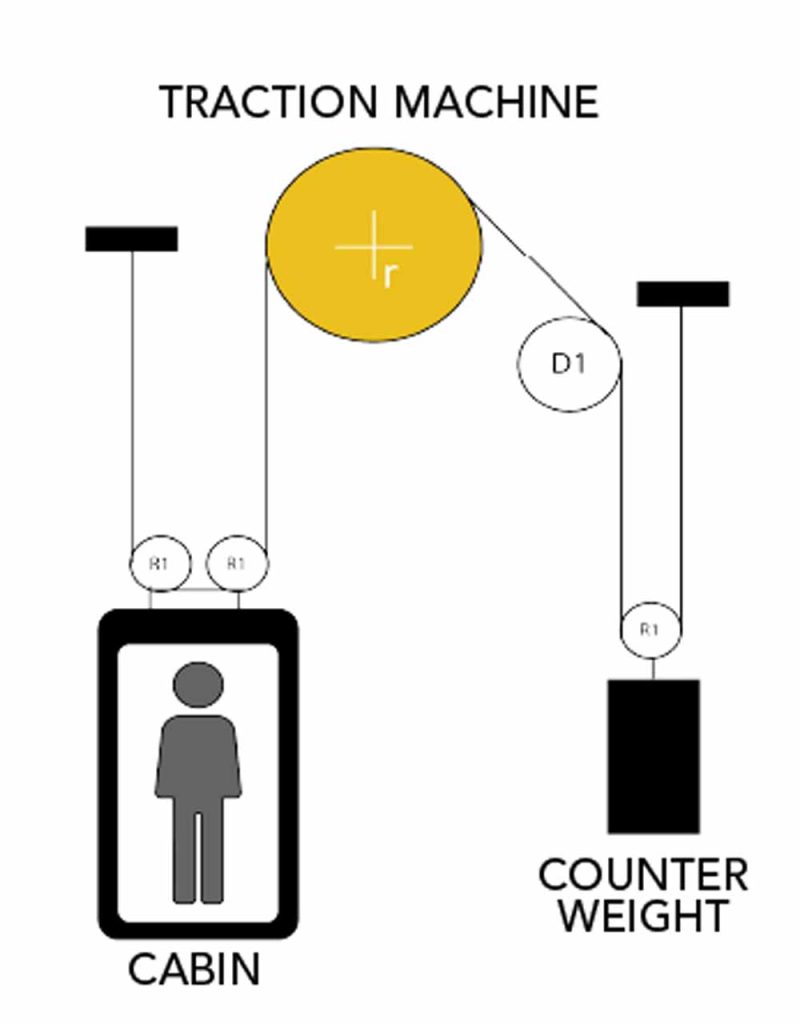
Another important consequence of using a smaller pulley is that the rotational speed (RPM) increases.

Generally, an increase in RPM leads to improved efficiency of the gearless itself, thereby reducing overall energy consumption.
Improved Energy Efficiency
The RPM of the pulley significantly impacts the efficiency of the gearless motor. A smaller pulley diameter results in higher rotational speeds for a given cabin speed, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the machine. Let’s see why:
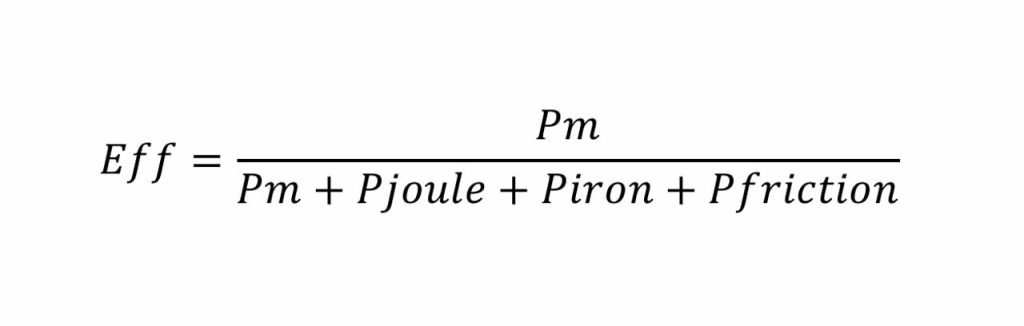
Where:
Eff: motor efficiency
Pm: Motor power -> k· Torque · RPM
Pjoule: Motor joule losses
Piron: Motor iron losses
Pfriction: Motor frictions
Considering RPM lower than 800 RPM Piron and Pfriction are very low in comparison to Pjoule, we can neglect these terms:
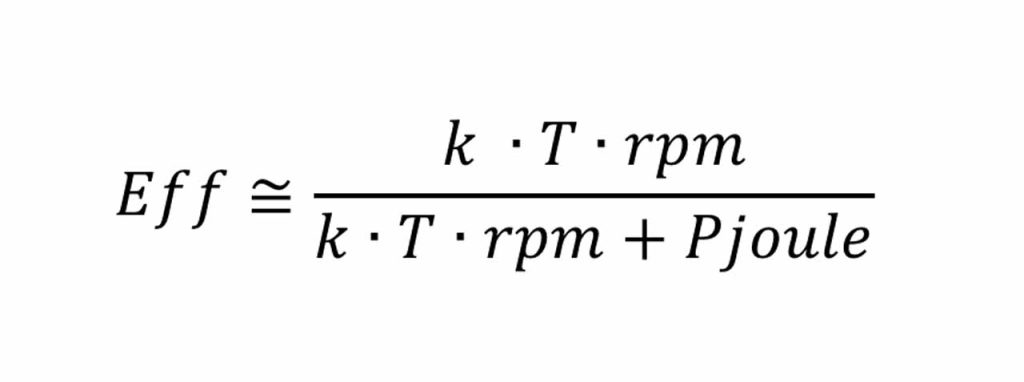
Considering two different motors having different nominal torque (and therefore different size) but the same current density and flux density (the same technology and same exploitation of materials), Joule losses depend directly on the copper volume.
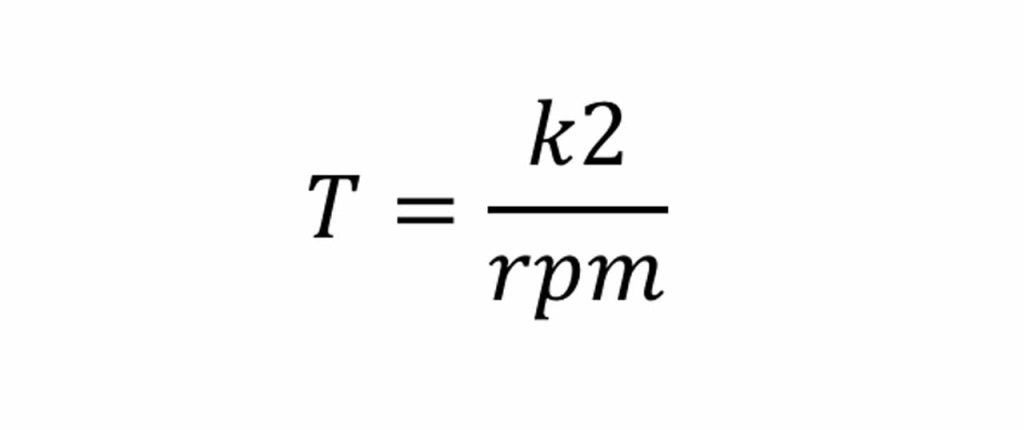
If we compare two identical elevators, where the only difference is the traction sheave diameter, we can write a relation between Torque and RPM:
Therefore:
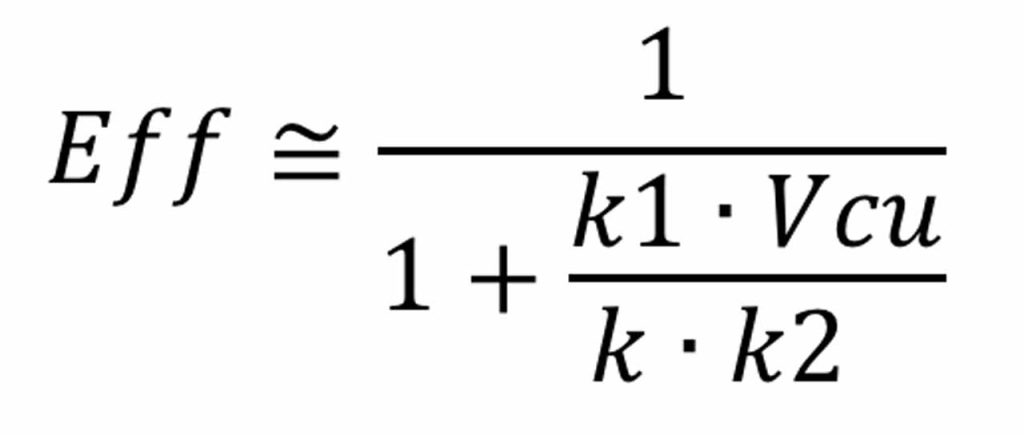
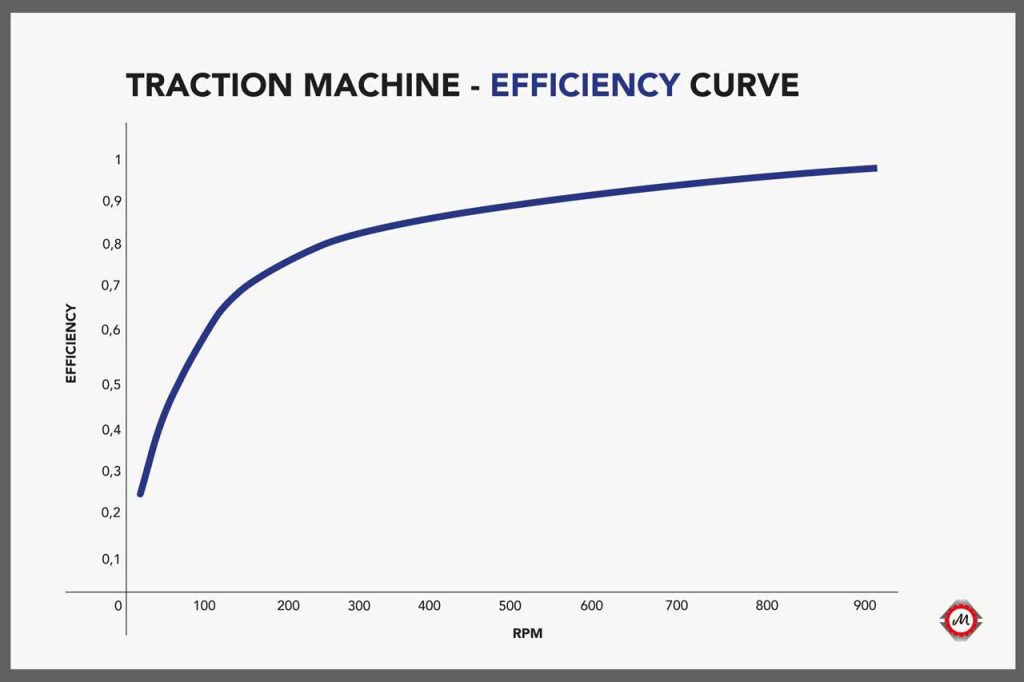
Since gearless with lower torque will have lower copper volume, efficiency from the above formula will be higher. Here is a typical efficiency curve:
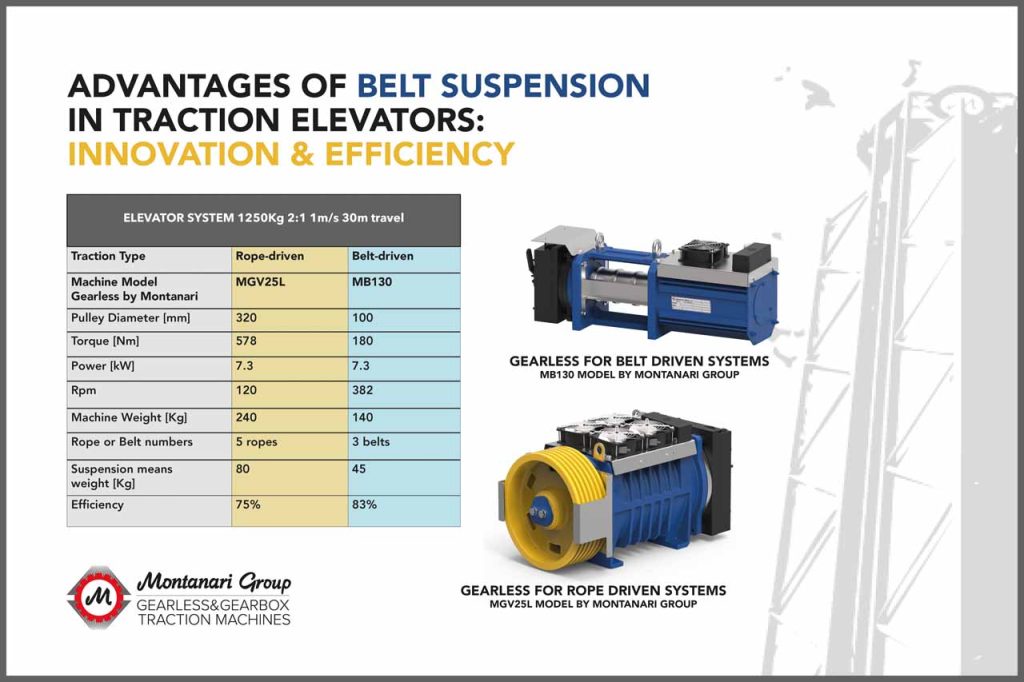
Below is a real example of two cases in which the same elevator is driven by two gearless motors having traction pulleys of different diameters: 320 mm with traditional ropes and 100 mm with belts.
From the table above, several aspects can be deduced:
- The torque of the belt-driven gearless motor is lower, and, indeed, the weight of this gearless motor is almost half compared to the one with the 320-mm pulley.
- The efficiency of the belt-driven gearless motor is significantly higher than that of the 320-mm pulley gearless motor.
- The powers of the two gearless motors are exactly the same, demonstrating that torque — not power — is the most important parameter that identifies an electric motor.
Reduction in Weight and Costs
Using smaller diameter pulleys results in significant torque reduction, allowing the use of lighter and more economical traction machines. The above practical example demonstrates how, with a smaller pulley, one can reduce the required torque, leading to substantial reductions in both the weight and cost of the gearless machine.
Advantages in Specific Applications
In machine-room-less and retrofit installations, where structural constraints are stricter, belt technology provides substantial benefits. Reduced machinery size and headroom space optimisation offer greater design flexibility, facilitating integration into existing buildings without the need for costly structural modifications.
Impact on Ride Comfort
Belt-driven systems significantly reduce noise and vibration, improving passenger comfort. This aspect is particularly valued in residential buildings, hotels and hospitals, where silence is a critical factor in evaluating elevator ride quality.
Flexibility For Modernisation
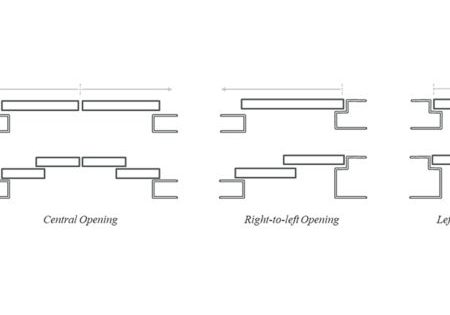
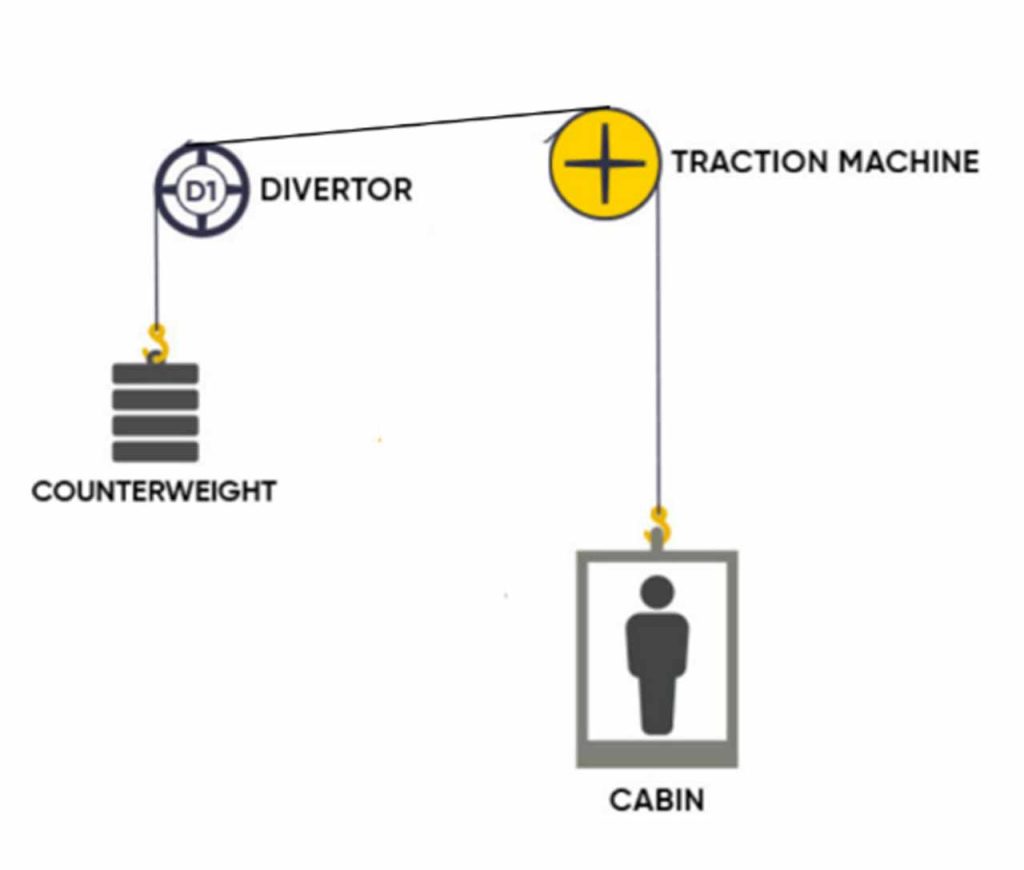
One of the most significant advantages of belt systems is their exceptional friction coefficient — two to three times higher than conventional steel ropes. This characteristic fundamentally changes the equation for traction calculations and opens new design possibilities.
With traditional steel ropes, achieving adequate traction typically requires wrap angles between 150° and 180°. The superior friction coefficient of belts allows for significantly reduced wrap angles (as low as 90° in some configurations). This solution enables the creation of a highly flexible modernisation approach capable of addressing a wide range of different situations.
Conclusion
The introduction of belt suspension systems represents a significant innovation in the elevator industry, capable of ensuring not only energy and cost savings but also enhanced passenger comfort. The ability to adopt extremely small pulleys constitutes a distinct competitive advantage, paving the way for innovative solutions tailored to all current and future market needs.
About Montanari Group
Montanari Group is specialised in the production of gearboxes, gearless, safety devices and accessories for lifting systems. Its U.K. distribution partner is Atwell International Ltd., which provides comprehensive technical support, access to the Montanari product range and after-sales service for lift installations and modernisations.
Get more of Elevator World. Sign up for our free e-newsletter.