The Smart Readiness Indicator and Lifts
Feb 1, 2022

To be or not to be included?
by Alper Caliskan
Buildings of the future, both office spaces and residential homes, will offer luxury and comfort that can only come from advances in modern technology, particularly in the area commonly referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT). These futuristic “smart” buildings may be packed with a range of internet-connected devices and sensors that cannot only tailor the environment according to the tastes and preferences of each individual but also analyze and predict usage patterns to save scarce resources such as energy and water and will contribute to the overall resilience and safety of the communities living in these buildings.
Smart buildings are already making their way into existence. One of the most notable examples is consulting firm Deloitte’s The Edge office building in Amsterdam, which analyzes 2,500 employees’ schedules and working patterns, allocating them workspaces suited to their specific daily needs. This highly sustainable building uses information technology to maximize not only the efficiency of the workspace but also the energy efficiency and safety of the building. The key to this is the analysis of the data collected, which helps keep coffee machines filled with beans and bathrooms clean during high-traffic periods. With the addition of solar panels installed on neighbouring buildings, The Edge now produces more energy than it consumes.
Smart technology offers significant energy savings and increased comfort and safety for the occupants of a building. Smart building sensors can, for instance, monitor the CO2 levels in a particular area of a building, and use this information to automatically increase or decrease ventilation levels. Occupancy sensors can also help manage heating and lighting levels without the need for human intervention and check the integrity of a building’s structure. Advanced energy systems can balance the load grid consumption to use more of what the building’s own solar or other renewable energy sources produce, or reduce consumption when demand from the national grid is high.
Across Europe, the building sector is now under pressure to increase the overall uptake of smart, energy-efficient technologies. This is expected to result in a significant reduction in carbon consumption and help improve occupant comfort and satisfaction levels. However, to make this change a reality that is beneficial for all, the building industry needs a trustworthy source of information and a common vocabulary for all stakeholders, such as occupants, investors, engineers, architects and component and equipment manufacturers.
What is the SRI and how is it calculated?
The Smart Readiness Indicator (SRI) for buildings is an optional EU policy initiative from the European Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD), and is intended to create smarter, healthier and more comfortable buildings with a lower energy use and carbon impact. The SRI is also designed to facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources in future building energy systems.
Across Europe, the building sector is now under pressure to increase the overall uptake of smart, energy-efficient technologies.
The SRI delegated and implementing acts were published in December 2020 and entered into force in January 2021, a key milestone in the EU strategy to make its building stock futureproof. The SRI rating is an overall top-level indicator that is calculated by various factors in three main categories: (i) energy savings and maintenance, (ii) comfort, ease and wellbeing and (iii) grid flexibility.
Many questions remain about the SRI’s implementation in EU countries, which is currently being tested. The debate revolves around a range of topics, such as:
- whether the assessment should be made mandatory for all buildings
- whether self-declaration or third-party inspections are the best methodology to be used for assessments
- what additional elements should be considered for inclusion in the index.
How does the SRI benefit stakeholders?
For occupants, the benefits of living or working in a smart building with a high SRI rating are clear. From a smartphone app, users can switch lighting, heating, air purification systems and even coffee machines on before they get home. The system may even be able to do this for the user automatically based on location services and learned preferences.
Smart equipment in the residential home simply equates to comfort. The technology comes with the additional benefit of lower energy consumption, which in turn saves the resident money, thereby making cost savings the underlying motivation for adoption of this technology.
This type of smart technology can also be applied to lifts in the building. Users can call the lift in advance, eliminating the need to touch buttons. Where appropriate, lifts can also be reserved for single-person occupancy only, giving users greater peace of mind about the spread of transmissible illnesses. Indirectly, the use of smart technologies is also a great contributor to enhancing the level of safety in buildings, which is not considered in the EU SRI policy.
Equipment providers need fewer technicians to carry out physical equipment checks, maintenance and inspections, as this can be done virtually and monitored by software. There is less time needed to repair, less waste to the environment and less travel limiting CO2 impacts while enabling a full lifecycle assessment of components.
For property developers and facility managers, having a building with an A classification will help drive sales. Secondly, predictive maintenance and sensors mean that the cost of maintaining equipment is reduced. From this, there is also the additional benefit of increased safety.
From a governmental perspective, the SRI is beneficial because it will be another tool governments can use to meet the COP 21 Paris Agreement targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a very strong incentive for many European countries to reduce overall environmental impact from the building sector, which has remained largely unchanged in recent years, mainly due to rising demand for affordable new homes.

In terms of reducing environmental impact, the goal is to have a building that, instead of consuming energy from the grid, becomes a generator of energy, not only to the building itself but to the wider grid as well.
There are already many standards on sustainability and energy efficiency in the building sector, which the European Commission still needs to harmonize and optimize to eliminate overlap and conflicts.
Why are lifts not currently included in the SRI calculation?
During the consultation process, some stakeholders advocated for additional energy efficiency factors to be included in the calculation, such as “energy efficiency of the electrical installation,” according to IEC/EN 60364-8-1, or “energy efficiency of lifts and elevators.”
Energy efficiency itself is not part of the current scope of SRI, since the experts argue this would cause too much overlap with existing policy instruments such as Energy Performance Certificates and Energy Labels. Nevertheless, the “smart control” of such equipment could form part of the SRI calculation. For example, ventilation heat recovery efficiency is not part of the SRI, but the control of the ventilation rate – such as those based on CO2 sensors – is included in the index.
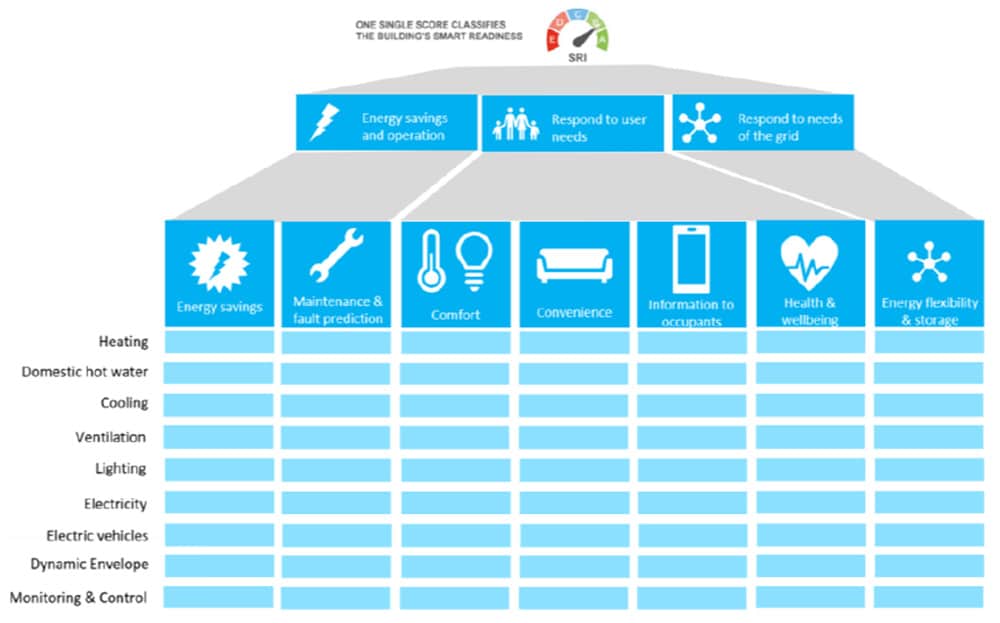
It was also suggested that the scope of smart services included in the SRI assessment should be broadened to include access control, fire alarms, security systems, lifts and elevators. The study team acknowledged that many of these services can provide smart functionalities to the building and its users. However, it was clarified they do not form part of the original scope of the SRI set by the EPBD mandate and, hence, were not included in the proposed streamlined methodology for the time being, although the technical study team has said it would be worthwhile to investigate future inclusion of some of these services in the SRI.
For this to be decided, many factors must first be carefully considered, such as the potential benefits and drawbacks of including additional services, other EU initiatives and measures where there may be some overlap, existing codes and standards and differences of opinion and uptake among EU member states.
The European Lift Association’s Role
Although the next date for the revision of the SRI legal instrument is yet to be confirmed, testing phases and discussions about improvements to the scheme are well underway. A working group called Topical Group C is currently investigating possible future additions and amendments to the SRI, and the European Lift Association (ELA) is represented within this group as a contributor and stakeholder.
Although the next SRI is only likely to come into effect in the next five years or so, ELA is already focused on its responsibility to arrive at a position on the inclusion of lifts in the index. As the voice of the lift, escalator and moving walk industry in Europe, ELA is consulting with its leadership and members through its interdisciplinary SRI Working Group and contributing to SRI Topical Group C to better understand the practical implications, opportunities and drawbacks of the proposed inclusion.
Conclusion
There are various existing EU initiatives surrounding lift certifications and energy efficiency, and for the SRI to be successful, it should not infringe or exist in parallel with these. The SRI has also been criticized by some commentators as being too heavily focused on energy efficiency when compared to consumer drivers around convenience and comfort. Policymakers will want to avoid fragmentation of the market and a lack of credibility, and will also prefer the EU to have a harmonized approach regarding the implementation of the index.

The road toward the implementation of the SRI will no doubt be a bumpy one, and resolving the many questions around its usefulness is bound to take some years to answer. However, in the long term, it is hoped there will be strong and sensible motivating factors around the adoption of the index, such as optimized energy efficiency, predictive maintenance, improved comfort for occupants, improved safety and maintenance, as well as an overall reduction in carbon emissions from homes and offices.
Get more of Elevator World. Sign up for our free e-newsletter.









