NUCLEUS, an advanced elevator collective control system, improves elevator handling capacity and allows elevators to be used in fire evacuation.
by Hitoshi Aoki Elevator Laboratory , Ltd. Japan
ABSTRACT
Applying NUCLEUS to zoning system, we developed an advanced zoning system, having two independent systems, local system & access system. Each zone is served by a local system transporting passengers moving inside the zone, and an access system transporting passengers moving between the zone and a lobby. These systems consist of groups of 13people 2car with advanced collective control. Because of an efficient grouping of the small size 2 cars, the rentable ratio becomes larger than that of the sky lobby system. According to the improvement of the evacuation time and unnecessary of the transfer at a sky lobby, passengers can evacuate safely at an initial fire.
INTRODUCTION
It is necessary to use elevators for evacuation during fire, especially for following four kind of buildings, (1) hospitals and welfare institutions where many users can not evacuate without using the elevator, (2) facilities where users being unable to take refuge via stairs may enter by making to barrier-free (3) apartment houses where residents grow old, (4) high-rise buildings where evacuation by using elevator is faster than that via stairs in whole building evacuation.
Although using elevators for evacuation during fire is beneficial, the handling capacity of the elevator system is limited.
Architectural Institute of Japan (2009) recommends the method only selected evacuees can use elevators but others must evacuate via stairs. And the method is applied only to the facilities that have enough number of administers to select proper evacuees using elevators and induce them to evacuate safely in order. And McColl (2009) mentioned a new process, the Emergency Evacuation Operation (EEO). This process would provide elevator operation for egress from five affected floors: the fire floor, and the two floors above and two floors below the fire floor. In case of fire, smoke and gases would spread to upper floors via stair shafts and other spaces at first. Accumulated smoke fills upper floors, then descend downward, resulting that smoke spread to whole building in the event of delay. In order to avoid suffering from frame and the harmful smoke and gases, it is necessary to develop the fire evacuation operation that improves the handling capacity of the elevator system and the evacuation plan for all residents to evacuate by using elevators during fire.
CONVENTIONAL ELEVATOR SYSTEM
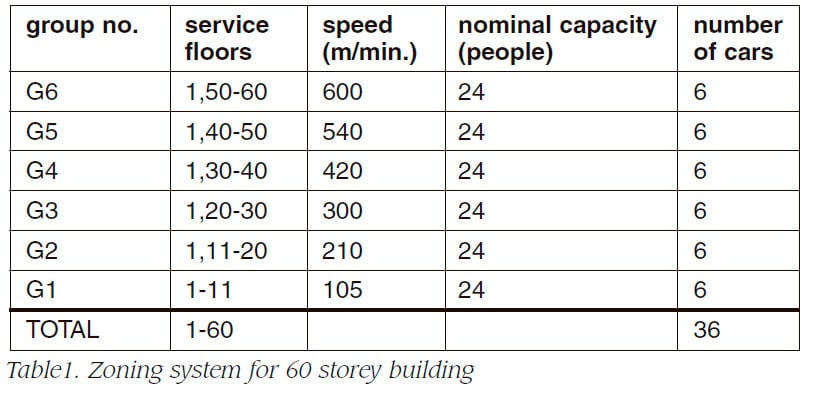
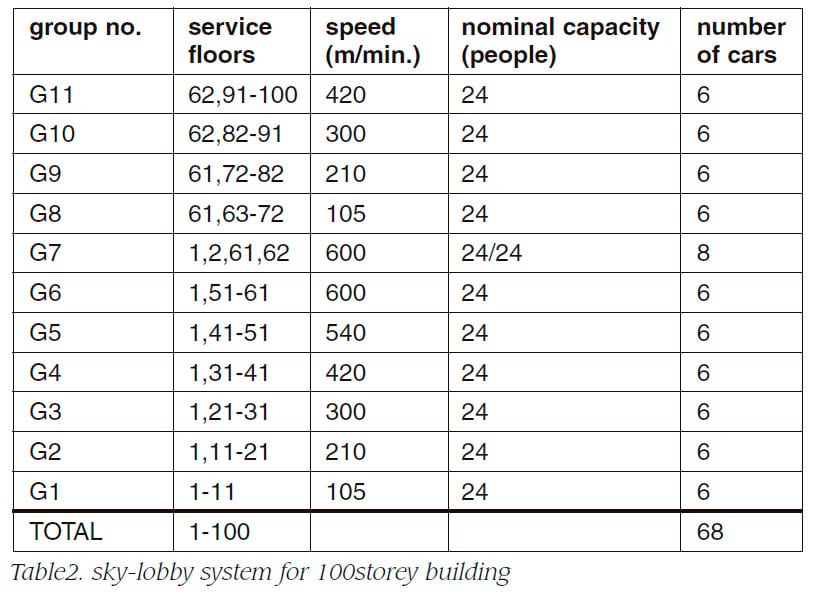
In case of conventional elevator system, a zone is served by a group of elevators. Because the number of elevators in a group is eight at most, a single zone system can manage less than 20 story buildings. Taller buildings are applied with zoning system. Table1 shows the specification of a zoning system applied to 60 story building. Where, floor 11, In case of conventional elevator system, a zone is served by a group of elevators. Because the number of elevators in a group is eight at most, a single zone system can manage less than 20 storey buildings. Taller buildings are applied with zoning system. Table1 shows the specification of a zoning system applied to 60 storey building. Where, floor 11, 20,30,40,50 are transfer floors. In zoning system, the occupation area increases as the height of building rises. Therefore the rentable-ratio becomes unacceptable in most cases, when the height exceeds 60 storey. In order to resolve this issue, high-rise buildings taller than 60 storey are applied with sky-lobby system. Table 2 shows the specification of a sky-lobby system applied to 100 storey building.
NUCLEUS
3.1 Advanced Collective Control
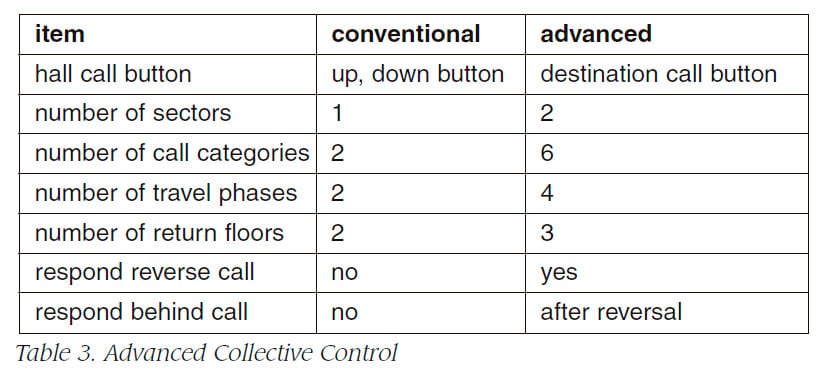
In NUCLEUS, all elevators are controlled with advanced collective control. Table 3 shows the differences between the advanced collective control and the conventional collective control.
3.2 NUCLEUS
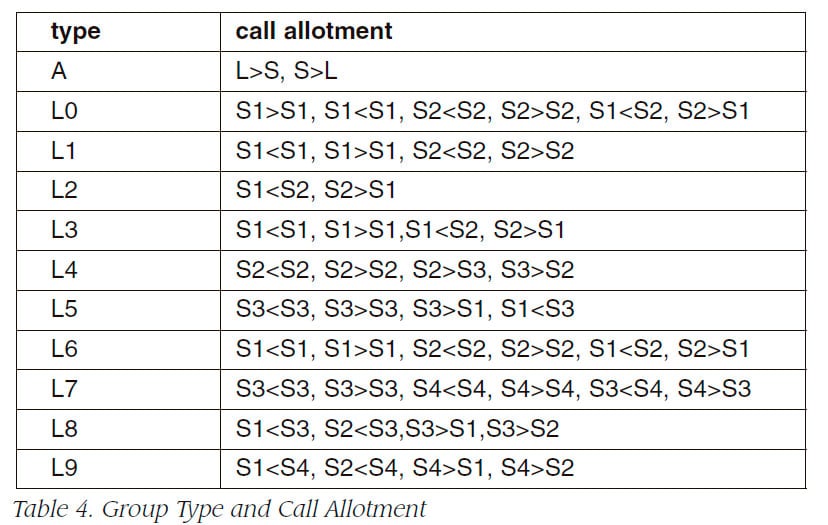
NUCLEUS is an elevator system where each zone is served by a local system transporting passengers moving inside the zone, and an access system transporting passengers moving between the zone and a lobby. The access system consists of plural number of group (A) s of elevators, where each group has its serving sector (S). And the local system may be L0 with a group (L0) of elevators or L1+L2 with 2 groups (L1) and (L2) of elevators or L3+L4+L5 with 3 groups (L3), (L4) and (L5) of elevators or L6+L7+L8+L9 with 4 groups (L6),(L7), (L8) and (L9) of elevators. Table 4 shows the type and the call allotment. Here, S1>S1 means calls originated at the floor in the sector S1 and the destination floor is lower floor in the sector S1.
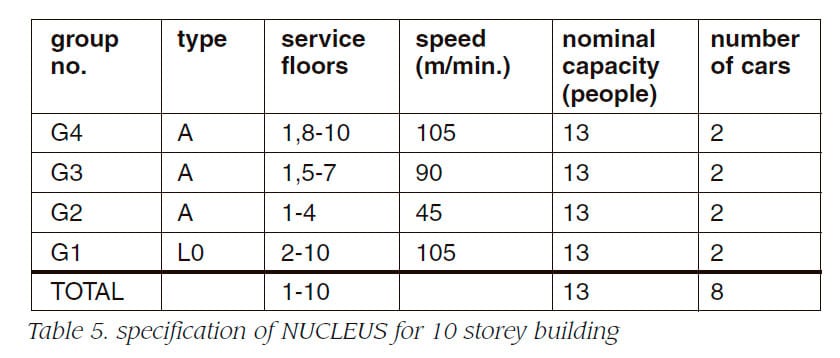
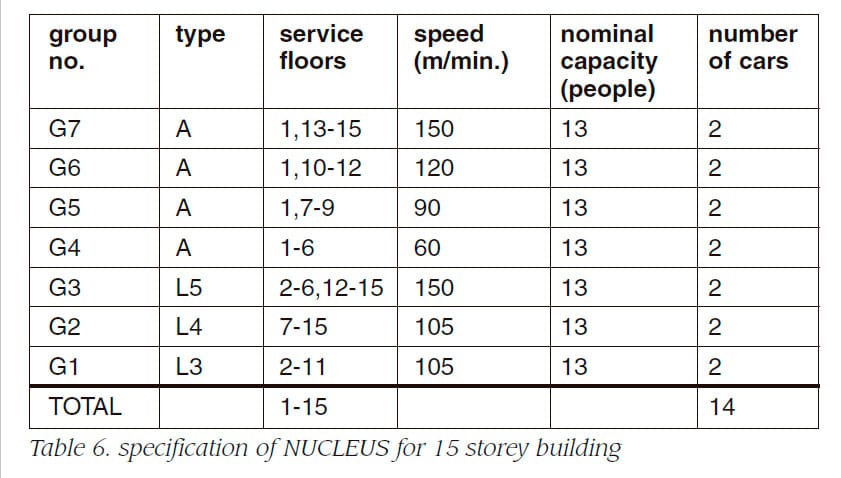
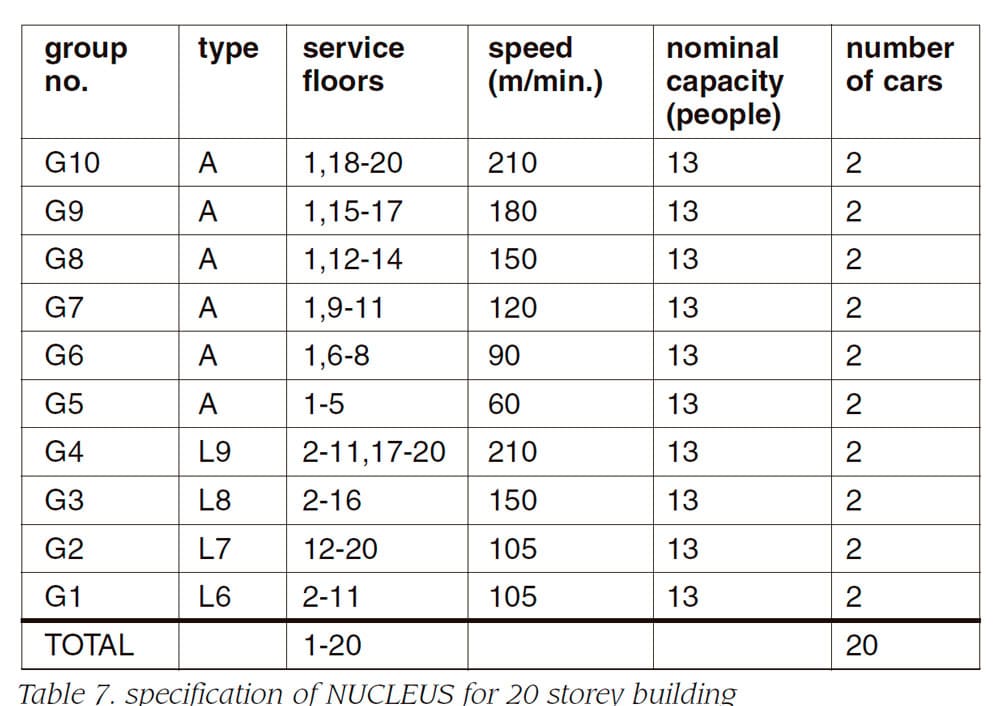
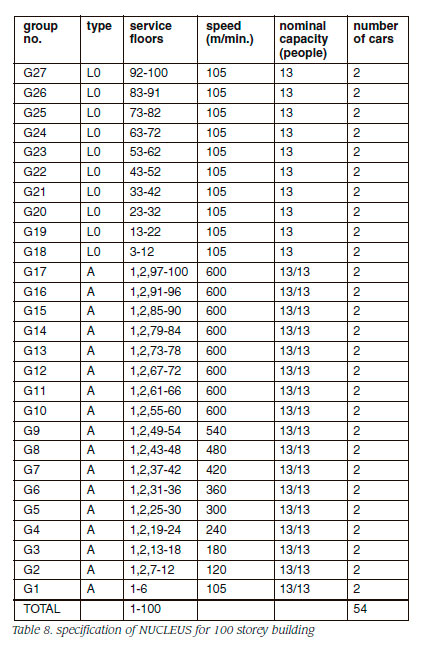
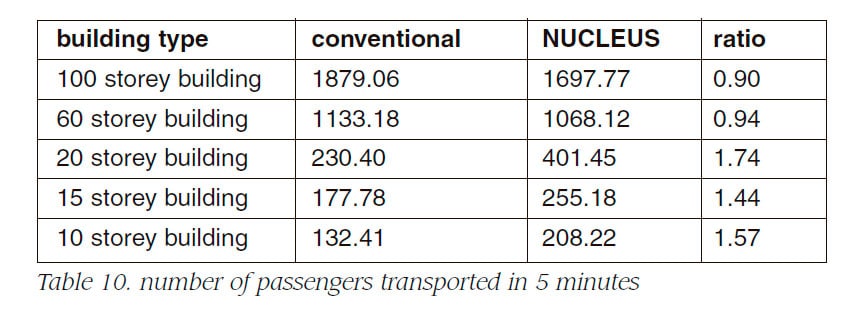
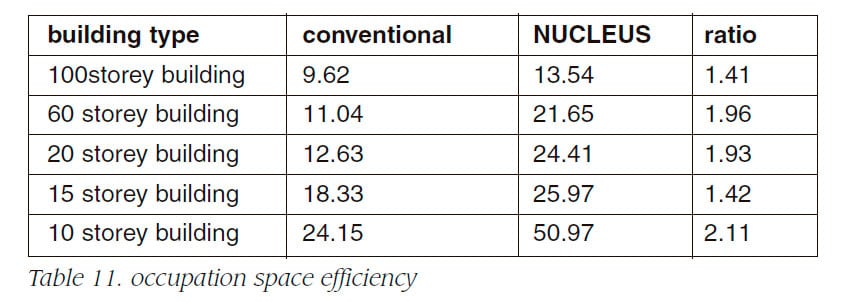
Table 5, 6, 7 and 8 show the specification of NUCLEUS for 10, 15, 20, 100 storey buildings, respectively. Advanced zoning system uses double decker as the access system.
3.3 Improvement of Rentable ratio
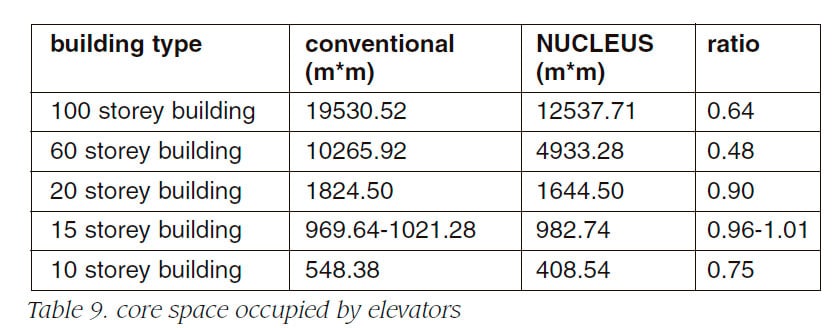
Table 9 shows the occupation area of NUCLEUS com-pared with conventional system. As occupation decreases, rentable ratio is improved.
EVACUATION OPERATION
4.1 Fire Evacuation Operation
Higher floor has higher priority because smoke and gases fills the upper floors, then descend downward. In order to maximize the handling capacity, the elevator serves floor by floor from the highest call.
4.2 Evacuation Time of Sky-lobby System
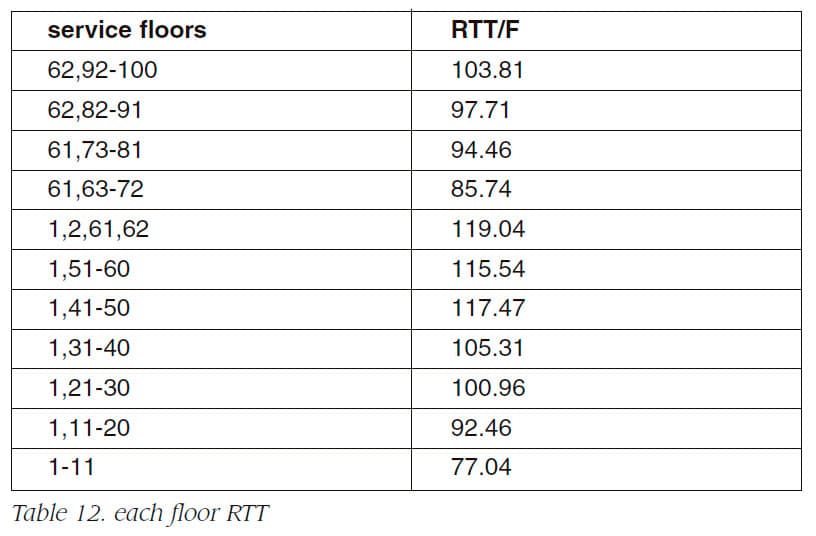
Table 12 shows the average time of round trip between lobby and each floor (RTT) of each zone in 100 storey building. From upper floors, there are 624/103.81+ 624/97.71=2.86 persons arriving at sky lobby (floor 62) in a second. And there are 624/94.46+624/85.74=3.20 persons arriving at sky lobby (floor 61) in a second. On the other hand, there are 8*24/117.47=1.63 persons each departing from each sky lobby in a second. Therefore, at floor 61, there remains 1.57 persons in a second, and at floor 62, there remains 1.23 persons in a second. Here, the number of residents in each floor is supposed to be P persons. Since evacuees from 19 floors arrive at each sky lobby, 19P persons arrive at each sky lobby. It takes 19P/3.2 seconds and 19P/2.86 seconds to transport 19P persons to floor 61 and floor 62, respectively. Therefore, regarding the completion of arriving 19P persons, completion time of floor 61 (t1) is faster than the completion time of floor 62 (t2).at 19P/3.2(t1),19P persons complete arriving at floor 61, then, another 19P persons complete arriving at floor 62 at (19P/2.86-19P/3.2) seconds later. During the interval (from0 to t1), there remains 19P/3.21.57=9.32P persons at floor 61, and during the interval(from t1 to t2),1.63(19P/2.86-19P/3.2)=1.15P per-sons depart from floor 61, so there remains9.32P-1.15P=8.17P persons at floor 61. As for floor 62, there remains 19P/2.861.57=10.43P. It is the man problem of the sky lobby system that a large amount of evacuees may stay at sky lobbies. Because, in case of sky lobby system, shuttle elevators are bottle neck of the system., The evacuation time equals to the evacuation time of the shuttle elevators. Therefore the evacuation time of sky lobby system is 19P/8/24119.04=11.78P seconds.
4.3 Evacuation Time of Adaptive Zoning System.
Regarding the group of 2cars serving 91 to 96 which has the longest evacuation time, the evacuation time becomes 3P/13/2122.64=14.15P, when applying 600m/min(RTT=122.64). If adequate speed such as 1000 m/min (RTT=101.44) is applied, it becomes 11.70P, which is faster than the evacuation time of sky lobby system (11.78P). And, the evacuation can be completed in an hour, if P is less than 305.6 persons.
EVACUATION PLANNING
5.1 Level Evacuation Place
In order not only to make evacuation process simple, but also to simplify the announcement system, we introduce the level evacuation place, where evacuees of the floor temporarily stay and wait for the elevators to evacuate to the lobby. In order to constitute the level evacua-tion place, a pair of fire prevention shutters are installed including two landing doors of access system between them, to partition from fire site. As a result, a group of elevators of the access system serving the floor become to be installed adjacent to the level evacuation place. Since seven evacuees can stay in a square meter by analogy with cage of 24 people elevator, the capacity of the level evacuation place is 280, if the width of the corridor is 4 meters and the distance between the shutters is 10 meters. The shutters can prevent fire for an hour.
5.2 Evacuation Scenario
Once, fire detector being activated, residents of the building are announce to take refuge in the level evacuation place. Then, elevators of access system start to transport evacuees staying in the level evacuation place to the lobby repeatedly by the fire evacuation operation.
Evacuees can wait safely in the level evacuation place and get on the elevators arriving adjacent to the level evacuation place without con-fusion.
CONCLUSION
By utilizing NUCLEUS, elevators can be used for evacuation during fire, even in the buildings where users are unspecified . It is inevitable that the advanced zoning system will take place of the sky lobby system for a skyscraper in a near future. Therefore, requirements for faster than 600m/min.may increase.
REFERENCES
Architectural Institute of Japan (2009).
Guideline on evacuation Planning for Using Elevators During a Fire. Maruzen, Tokyo. pp87.
David McColl(2009). Use of Elevators during Emergencies, Elevator World, Vol.57(1), pp26-28.
David Nicholson(2009). Using Elevators to Evacuate High Rise Buildings, Elevator World, Vol.57(10), pp154-162
Get more of Elevator World. Sign up for our free e-newsletter.