Paul Schuyler Van Bloem
Feb 1, 2016

Research of eclectic inventor reveals advances in the early elevator indicator.
ELEVATOR WORLD receives numerous requests for information throughout the year from people outside of the industry seeking information about old elevator systems and related technology. While these requests are often easily and quickly addressed by EW staff, occasionally, a question requires more extensive research. Such was the case with an inquiry that came to EW in October 2015 regarding an old indicator (Figure 1). Fortunately, the indicator featured a manufacturer’s plate that included a list of relevant patents, which provided an excellent starting point for pursuing additional information (Figure 2). However, this seemingly straightforward beginning quickly led to unexpected results and an investigation that eventually revealed an intriguing individual, who, for a brief time, applied his considerable inventive and creative skills to the world of vertical transportation.
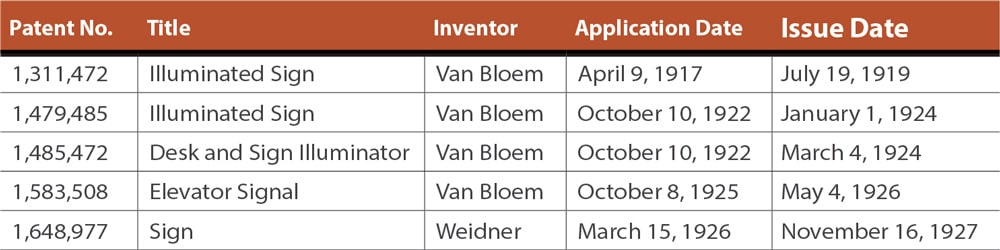
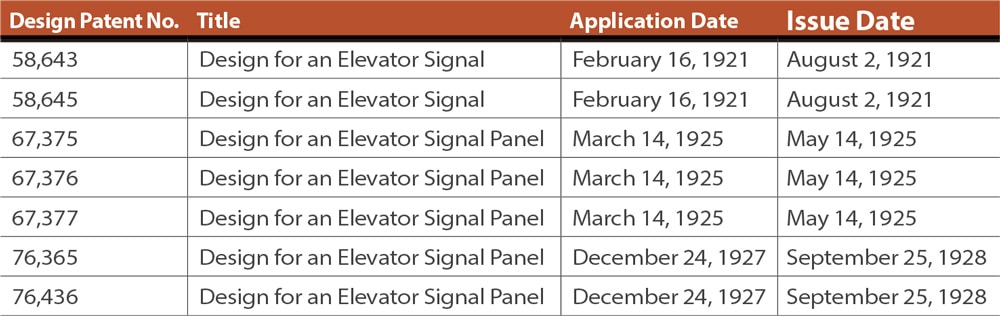
The manufacturer’s plate identified the company as Viking Products. An examination of the patents revealed the company’s full name, Viking Products Corp., and the names of two inventors: Victor Weidner and Paul Schuyler Van Bloem (Table 1).
The fact that Van Bloem was credited with four of the five patents appears to establish him as one of Viking Products’ lead engineers, which prompts the question, “Who was he?” Van Bloem was born in Bayonne, New Jersey, in 1892 and attended Curtis High School on Staten Island. Founded in 1904, the school apparently specialized in vocational and industrial training courses. Van Bloem’s high-school education was supplemented by private tutoring in engineering.[1]
Following graduation, he worked for a series of well-known New York architects and architectural firms: William Lee Stoddart (1911), Warren & Wetmore (1912) and William Welles Bosworth (1912-1917). In his first two positions, he worked as a draftsman. In Bosworth’s office, he was apparently an office manager “in charge of all construction.”[1] In 1917, Van Bloem, Lawrence L. Strauss and Jesse Acker established Viking Sign Co. Van Bloem served as president, and the new company’s board of directors included Bosworth. In February 1923, the company name was changed to Viking Products Corp. with Van Bloem serving as president and general manager.
Thus, Van Bloem’s engineering education was limited to high-school courses and private tutoring, and his early activities clearly imply that he planned to pursue a career in either architecture or building construction. No evidence has been found that explains why he decided to change his focus and establish a company devoted to the design and manufacture of electric signs. Nonetheless, following the founding of Viking Sign, he immediately displayed a remarkable understanding of electric lights and lighting design. Between 1917 and 1935, Van Bloem filed 16 patent applications for electric signs, seven of which concerned elevator signals (Table 2).
In his first two patents, Van Bloem used almost identical language to describe the perceived problem with contemporary signal designs:
“Elevators in large buildings are usually arranged in banks or groups in a corridor. Frequently, the elevators are arranged on opposite sides of the corridor. The up and down signals, which indicate the direction of travel of the elevator, are usually supported by means projecting beyond the wall of the corridor above the elevator doors. These signals as ordinarily arranged are automatically lighted through a contact device actuated by the movement of the elevator in the shaft to indicate whether the elevator is traveling up or down. Signals of this type present many difficulties. They are difficult to understand instantaneously; require thought of interpretation of their meaning; are usually unsightly; and are not, as a general rule, well adapted for the purpose of directing the waiting passenger to the oncoming elevators. This is due to the fact that they are not in themselves of such form as to impel the waiting passenger to move to the door of the oncoming elevator.”[2]
This analysis of the operational characteristics of elevator signal lights followed the same logic used by Van Bloem in a paper presented to the Electrical Association of New York in April 1922. The paper, tilted “A Survey, Comparison and Classification of Indoor Electric Signs,” outlined the key “factors” associated with “bringing about the greater use” of electric signs in buildings:
“The complexity of the modern building, with its maze of corridors and passageways, demands the rapid introduction of effective ways of educating the public. Increasing competition among merchants is bringing about the greater use of indoor signs to induce sales, to promote good will and to give customers every advantage of service and convenience. City ordinances, such as zoning laws and fire prevention laws, demand the use of a device to quickly attract the attention of people. The indoor electric sign has so far shown itself to be the most effective and persuasive medium for this message.”[3]
His emphasis on the need for clarity and for signs to “impel the waiting passenger” toward the desired location, coupled with his perception of electric signs as a “persuasive medium,” highlight Van Bloem’s sophisticated understanding of visual communication strategies. Although his initial designs failed to fully live up to the expectations expressed in his patent text and presentation, they more than matched the quality of contemporary designs (Figure 3).
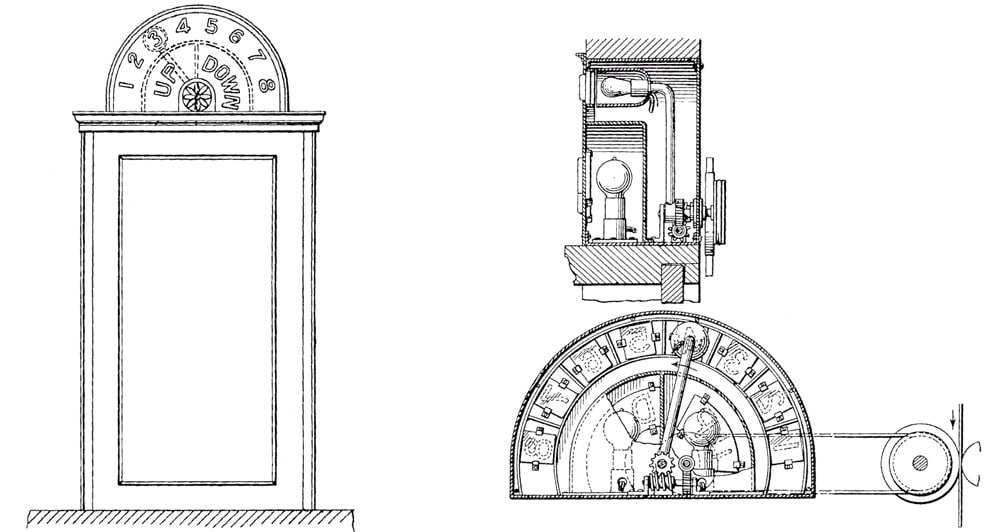
Van Bloem’s third elevator patent was the only one that concerned a lighted indicator system designed to show the precise car location. It followed a normative pattern with a semicircular panel above the elevator door with numbers that were illuminated as the car passed the corresponding floor. Although waiting passengers would have been able to discern the motion of the car by the order in which the numbers were illuminated (ascending or descending), Van Bloem also included “up” and “down” indicators in his design (Figures 4 and 5).
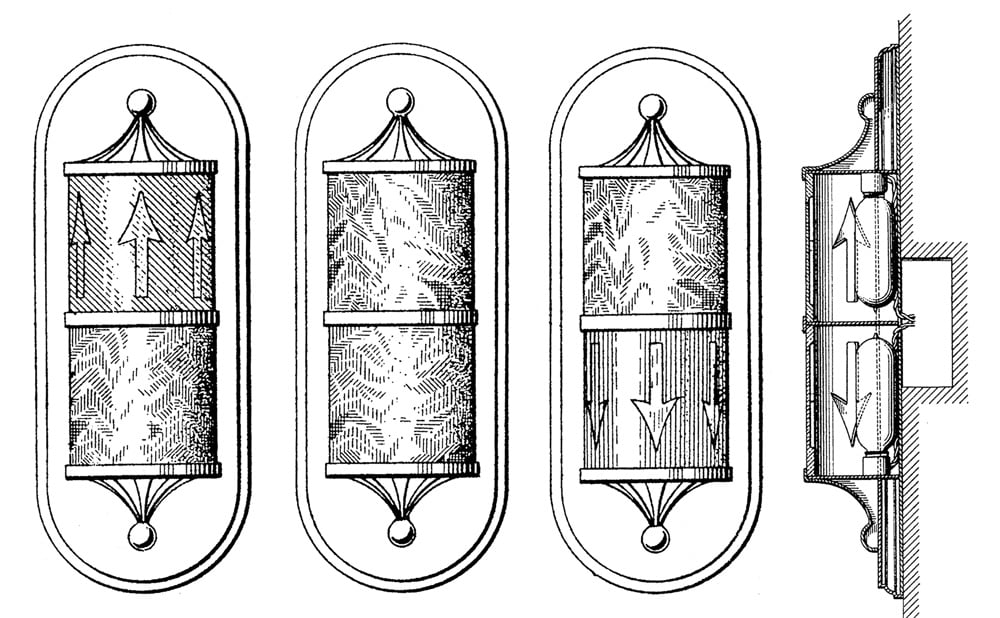
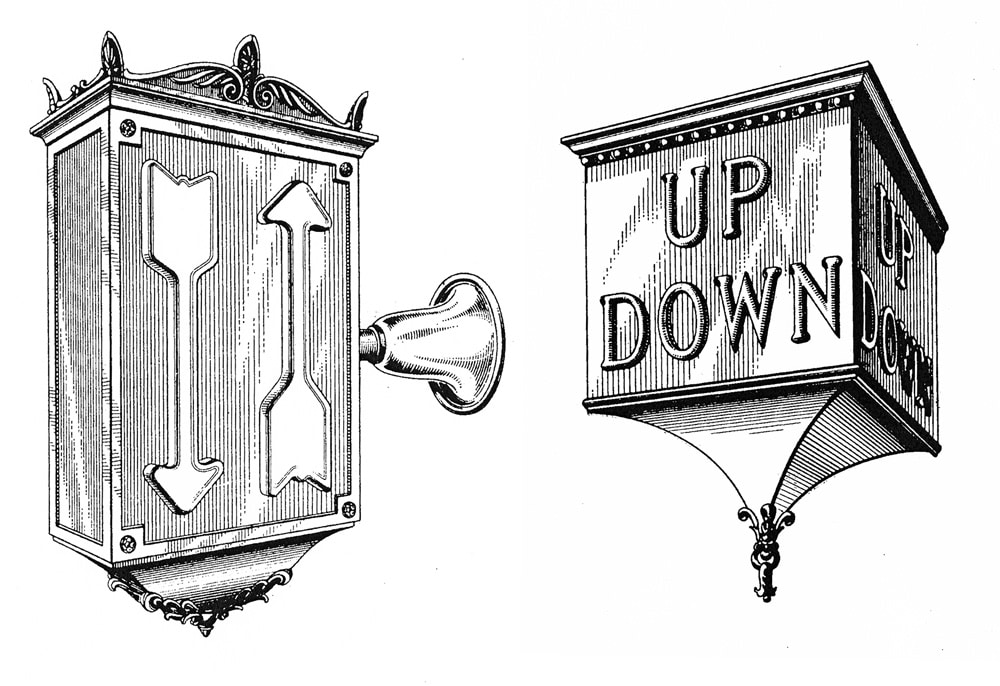
In his next three patents, Van Bloem returned to directional lights, which were intended to indicate “the approach of an elevator car and the direction of its travel.”[4] His designs were also intended to “provide an elevator signal of simple form, which, when unilluminated, will be inconspicuous but which, when illuminated upon the approach of an elevator car, will be rendered very conspicuous and will distinctly indicate the direction of travel of the car.”[4] Two designs were flush-mounted lights similar to those found in his first patents, while the third concerned a cylindrical glass indicator (Figures 6 and 7). The latter was designed such that the up and down arrows were only visible when the proper section of the indicator was illuminated. Van Bloem’s description of this design included a reminder of typical indicator operational protocols:

“Elevator signals are usually mounted in pairs, one indicating the up-travel of the elevator car, and the other indicating the down-travel thereof. Up-and-down signals usually are differently colored, the up signal being usually white, although green frequently is used, and the down signal being usually red, although other colors are sometimes used. It is one of the important objects of this invention to so treat the exteriors of the receptacles or containers such that, with the lamps extinguished, both the up and down signals have the same general exterior appearance, and the color of the glass is concealed until the signal lamp is lighted.” [5]
His final signal patent concerned a system whereby the sign’s text would be invisible until illuminated from behind.
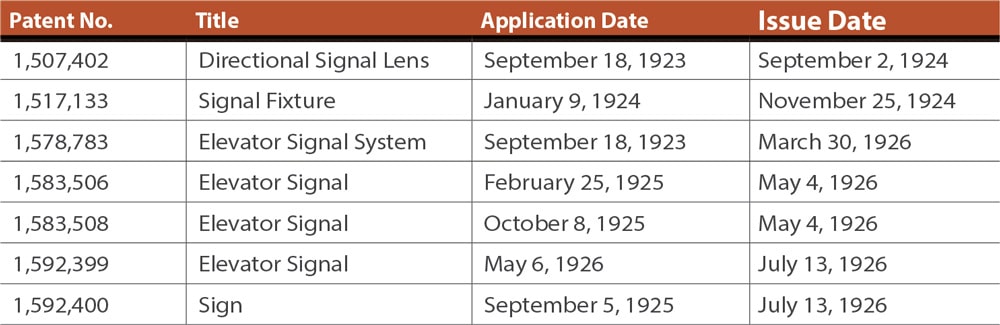
An examination of these patent drawings does not appear to provide an overt design link to the indicator that prompted this article. However, further investigation revealed that Van Bloem did not limit his design career to patenting inventions. He also received 15 design patents, seven of which concerned elevators (Table 3).
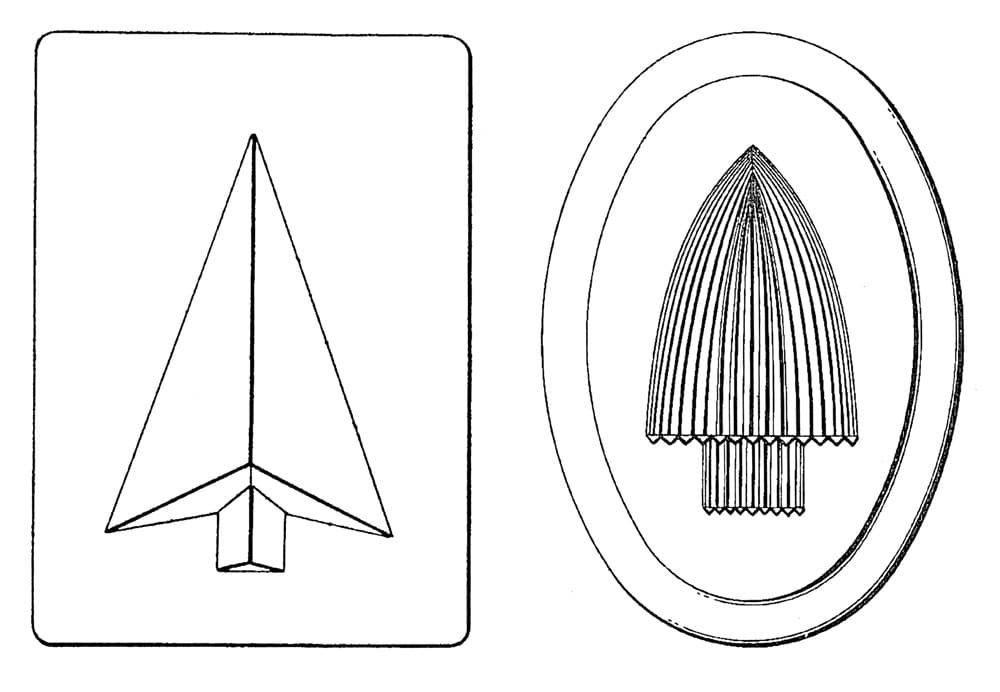
The designs for elevator signal panels concerned small wall-mounted indicators that would inform waiting passengers of the direction of travel (Figure 8). These had similar visual characteristics to the designs found in Van Bloem’s patents.
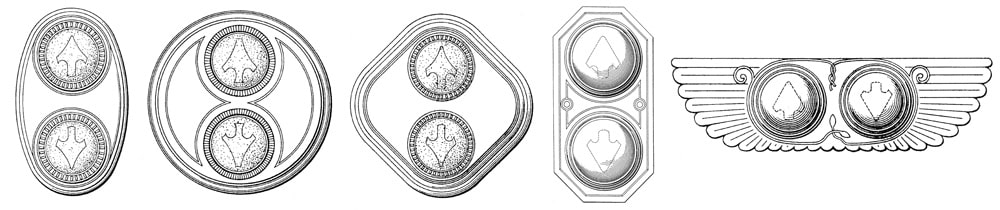
On the other hand, the two designs identified as elevator signals likely reveal the hand of the designer who produced the indicator that launched this investigation (Figure 9). This indicator’s origin was the former AT&T Headquarters Building located at 195 Broadway in New York City. The building was designed by William Welles Bosworth and built in two phases: 1912-1916 and 1920-1922. Thus, it appears Bosworth hired his former employee to provide elevator signals for the second phase of the building. However, the date of the final patent listed on the manufacturer’s plate, 1927, somewhat challenges this assumption, as the indicator was apparently installed approximately five years after the building’s completion.
This puzzle is, perhaps, matched by the fact that, following his focused encounter with elevator signal design, Van Bloem moved on to other interests. In fact, after 1939, he never pursued electric sign design of any kind. In 1939, he left Viking Products and worked as division manager for Industrial Products Development at Gotham Pressed Steel Corp. In 1941, he joined New York City general building contractor Brown & Matthews, Inc., where he worked until his retirement in 1964. (Van Boem died in 1967).
Finally, it is important to note that an Internet search for “Paul Schuyler Van Bloem” does yield quick results; however, these are not the kind one might imagine given his biography outlined thus far. For example: the September 3, 1949, issue of the Saturday Evening Post included an illustrated article coauthored by Van Bloem titled “What the Tennis Stars Did to Me.” The article’s introduction reads as follows: “For 22 years, the author has taken his lumps as a Forest Hills official. Now retiring, he speaks his mind about the most temperamental of all athletes.”[6] In addition to his many years as an official, Van Bloem had also served as president of Eastern Lawn Tennis Association, and he played a critical role in the overall development of professional tennis in the first half of the 20th century.
Acknowledgement
EW (and your humble historian) are grateful to Mark A. Goldstein for sharing his elevator indicator with us and prompting the investigation that produced this article.
References
[1] Who’s Who in Engineering: A Biographical Dictionary of the Engineering Profession, Fifth Edition, Lewis Historical Publishing Co.: New York (1941).
[2] Paul Schuyler Van Bloem. “Directional Sign Lens,” U.S. Patent No. 1,507,402 (September 2, 1924).
[3] Paul Schuyler Van Bloem. “A Survey, Comparison and Classification of Indoor Electric Signs,” Transactions of the Illuminating Society, Vol. 18 (January-December 1923).
[4] Paul Schuyler Van Bloem. “Elevator Signal,” U.S. Patent No. 1,583,506 (May 4, 1926).
[5] Paul Schuyler Van Bloem. “Elevator Signal,” U.S. Patent No. 1,592,399 (July 13, 1926).
[6] Paul Schuyler Van Bloem with Magruder Dobie. “What the Tennis Stars Did to Me,” Saturday Evening Post, September 3, 1949.
Get more of Elevator World. Sign up for our free e-newsletter.